BibTeX
@ARTICLE{Fan2024,
author={Fan, Mengjie and Yu, Jinlu and Weiskopf, Daniel and Cao, Nan and Wang, Huai-Yu and Zhou, Liang},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics},
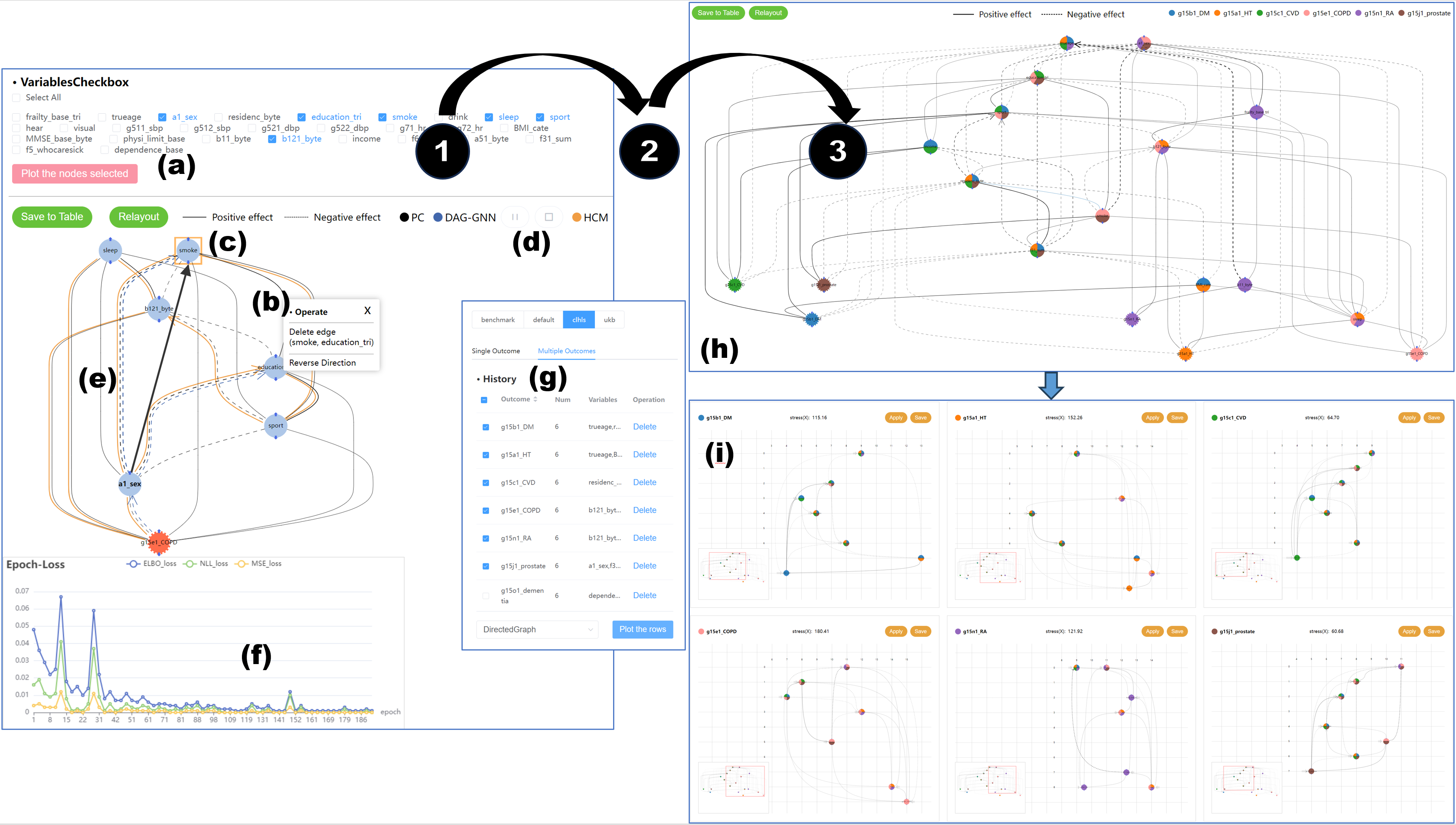
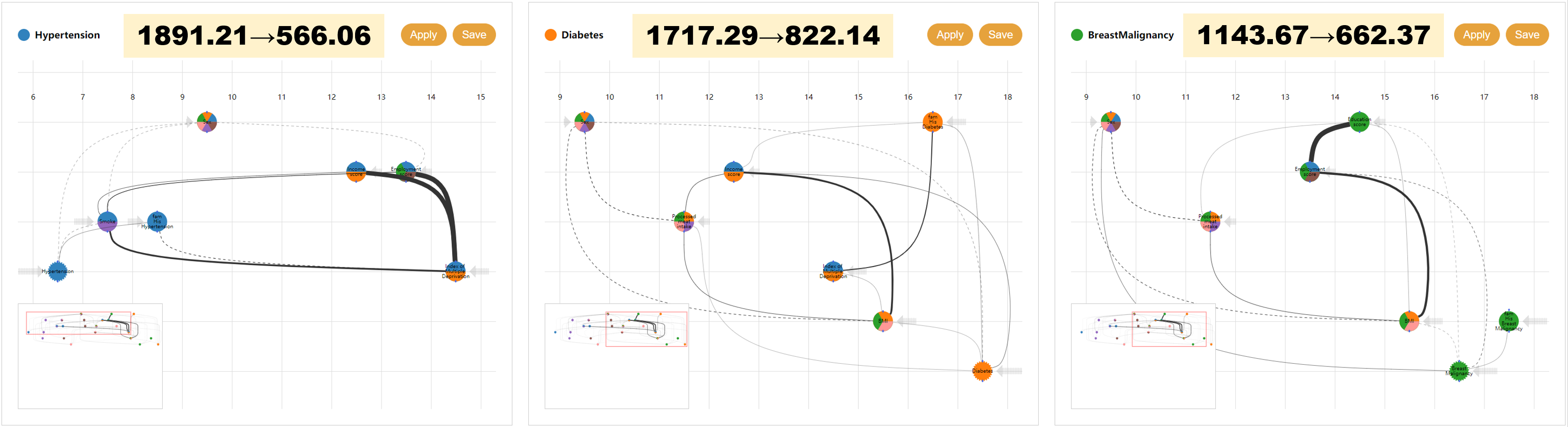
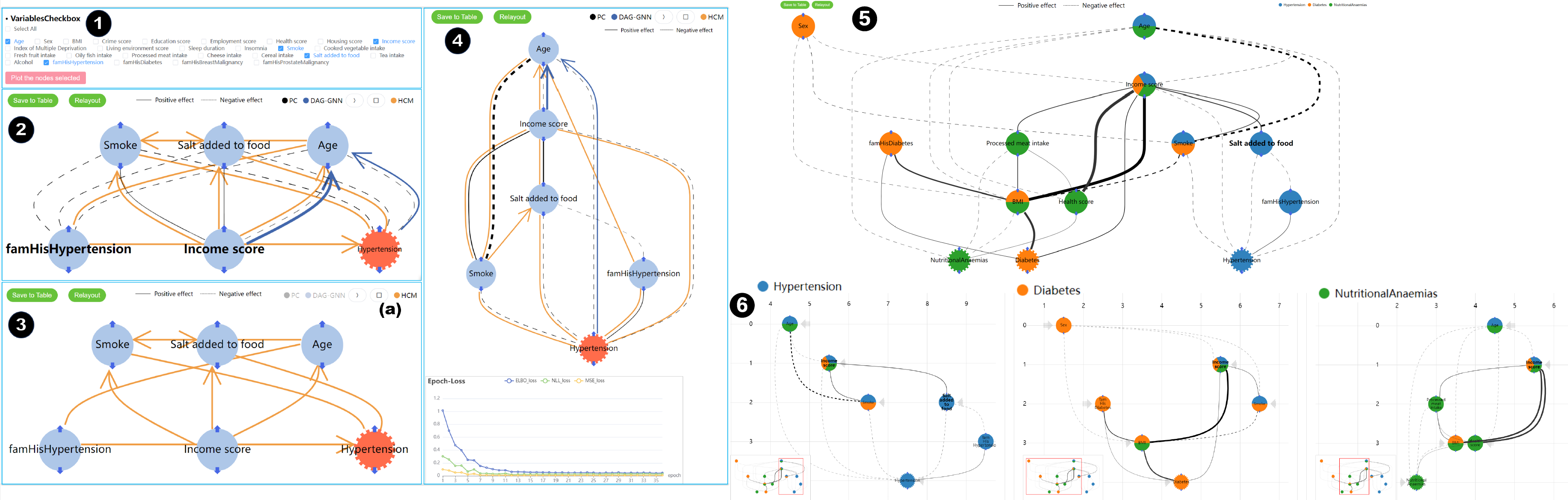
title={Visual Analysis of Multi-outcome Causal Graphs},
year={2024},
volume={},
number={},
pages={1-11},
keywords={Visualization;Data visualization;Layout;Cause effect analysis;Medical diagnostic imaging;Diseases;Cognition;Causal graph visualization and visual analysis;causal discovery;comparative visualization;visual analysis in medicine},
doi={10.1109/TVCG.2024.3456346}}